The Comprehensive Guide to Dog Food: Ensuring Optimal Nutrition for Your Pet

Choosing the right food for your dog is crucial for their health, longevity, and overall well-being. With a plethora of dog food options available, it can be overwhelming to determine the best choice for your furry friend. This comprehensive guide delves into the various types of dog food, their nutritional benefits, and tips for selecting the best diet for your dog. This guide aims to provide valuable information to dog owners seeking to enhance their pets' dietary regimen.
Section 1: Types of Dog Food
1. Dry Kibble: Dry kibble is one of the most popular types of dog food. It is convenient, cost-effective, and has a long shelf life. Kibble helps keep your dog’s teeth clean by reducing plaque buildup.
- Pros: Affordable, easy to store, promotes dental health.
- Cons: Can be low in moisture, may contain fillers and artificial additives.
2. Wet Food: Wet food, or canned food, has a high moisture content, making it an excellent option for hydration. It is typically more palatable for dogs, making it a good choice for picky eaters.
- Pros: High in moisture, more palatable, easier to chew.
- Cons: More expensive, shorter shelf life once opened, can contribute to dental issues if not managed properly.
3. Raw Diet: A raw diet, also known as BARF (Biologically Appropriate Raw Food), includes raw meat, bones, fruits, and vegetables. This diet aims to mimic what dogs would eat in the wild.
- Pros: High in protein, natural ingredients, can improve coat condition.
- Cons: Requires careful handling to avoid bacterial contamination, can be time-consuming and expensive, requires veterinary guidance.
4. Homemade Diet: Homemade dog food allows you to control the ingredients and ensure freshness. However, it requires careful planning to ensure a balanced diet.
- Pros: Complete control over ingredients, can be tailored to specific dietary needs.
- Cons: Time-consuming, requires knowledge of canine nutrition to ensure balance.
5. Dehydrated and Freeze-Dried Foods: These foods retain most of their nutrients by removing moisture. They need to be rehydrated before feeding.
- Pros: Long shelf life, retains nutritional content, easy to store.
- Cons: Expensive, requires rehydration.
6. Veterinary Prescription Diets: These diets are specifically formulated for dogs with certain medical conditions, such as kidney disease, allergies, or obesity.
- Pros: Tailored to specific health needs, usually backed by scientific research.
- Cons: Can be expensive, requires a prescription from a veterinarian.
Section 2: Essential Nutrients for Dogs
1. Proteins: Proteins are essential for growth, muscle repair, and overall health. They provide essential amino acids that dogs cannot produce on their own.
- Sources: Chicken, beef, lamb, fish, and eggs.
2. Fats: Fats provide energy, support cell function, and help absorb vitamins. They are essential for maintaining healthy skin and coat.
- Sources: Fish oil, chicken fat, flaxseed oil.
3. Carbohydrates: Carbohydrates supply energy and support digestive health. They should be part of a balanced diet but not the primary component.
- Sources: Brown rice, sweet potatoes, oats.
4. Vitamins and Minerals: Vitamins and minerals are vital for metabolic functions, immune health, and bone strength.
- Sources: Fruits, vegetables, and commercial dog food fortified with vitamins and minerals.
5. Water: Water is essential for all bodily functions. Ensure your dog has access to fresh water at all times to stay hydrated.
Section 3: Special Dietary Needs
1. Puppies: Puppies require more protein and fat to support rapid growth and development. Puppy-specific formulas are designed to meet these needs.
- Key Nutrients: High protein, DHA for brain development.
2. Senior Dogs: Older dogs may need fewer calories but more fiber and certain nutrients to support joint health and digestion.
- Key Nutrients: Glucosamine, chondroitin, higher fiber content.
3. Dogs with Allergies: Hypoallergenic diets with novel proteins and limited ingredients can help manage food allergies.
- Key Ingredients: Duck, venison, sweet potatoes.
4. Overweight Dogs: Weight management formulas are lower in calories and fat, higher in fiber to promote a feeling of fullness.
- Key Nutrients: Lower fat, higher fiber, L-carnitine.
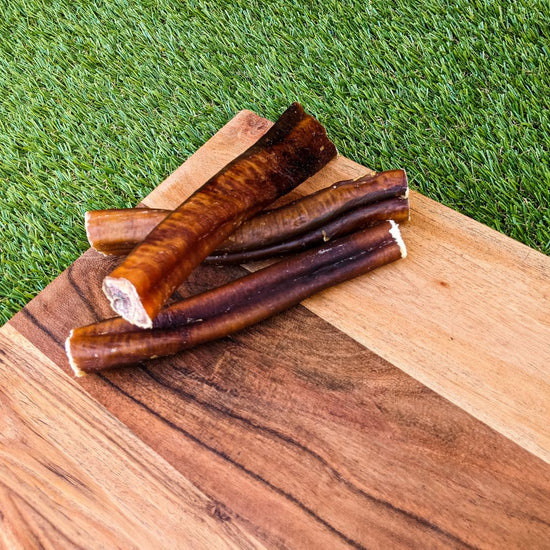
Section 4: Bully Sticks and Their Role in Dog Nutrition
1. What Are Bully Sticks? Bully sticks are natural dog chews made from the pizzle of bulls or steers. They are high in protein, low in fat, and easily digestible, making them a popular choice among dog owners.
2. Benefits of Bully Sticks:
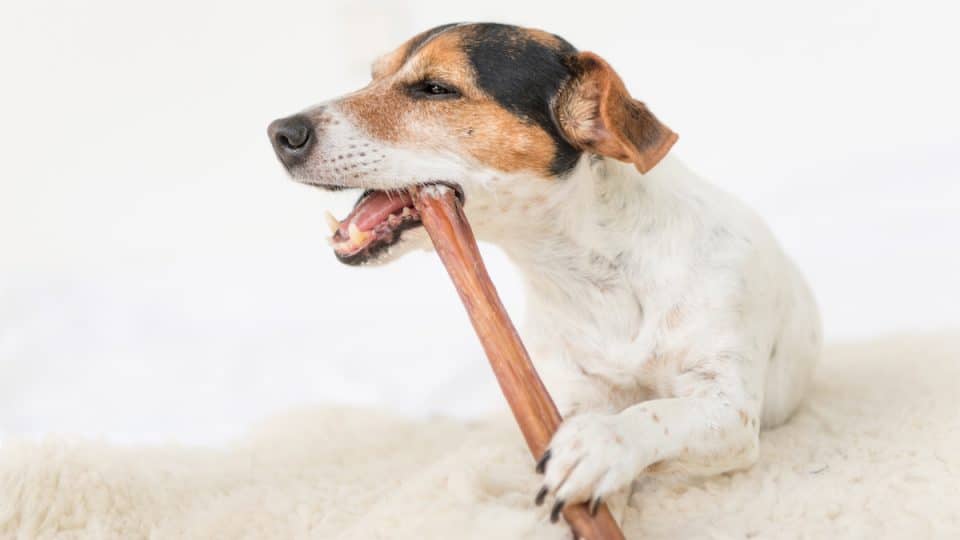
- Dental Health: Chewing on bully sticks helps reduce plaque and tartar buildup, promoting better dental health.
- Long-Lasting: Provides prolonged chewing satisfaction, which can help prevent destructive behaviors.
- Easily Digestible: Unlike rawhide, bully sticks are easily digestible and less likely to cause digestive issues.
- Mental Stimulation: Chewing provides mental stimulation and can help alleviate boredom and anxiety.
3. Choosing the Right Bully Stick:
- Size and Thickness: Select the right size and thickness based on your dog’s chewing style and size.
- Odor-Free Options: Some bully sticks are treated to reduce odor, making them more suitable for indoor use.
4. Safety Tips:
- Supervise Chewing: Always supervise your dog while they chew to prevent choking or ingestion of large pieces.
- Proper Storage: Store bully sticks in a cool, dry place to maintain freshness and prevent bacterial growth.
Section 5: Tips for Feeding Your Dog
1. Establish a Feeding Schedule: Consistent feeding times help regulate digestion and metabolism. Most dogs do well with two meals per day.
2. Measure Portions: Avoid overfeeding by measuring food portions accurately. Adjust portions based on your dog’s activity level and body condition.
3. Transitioning Foods: Gradually introduce new foods over a week to prevent digestive upset. Mix increasing amounts of the new food with decreasing amounts of the old food.
4. Monitor Weight and Health: Regularly check your dog’s weight and overall health. Consult your veterinarian for dietary adjustments based on health status.
5. Avoid Harmful Foods: Certain human foods can be toxic to dogs, including chocolate, grapes, onions, garlic, and xylitol. Ensure these foods are kept out of reach.
Conclusion
Providing your dog with a balanced and nutritious diet is essential for their overall health and well-being. Understanding the benefits of different types of dog food and bully sticks helps you make informed decisions about your pet's nutrition. Regular veterinary consultations and monitoring your dog’s health are crucial in maintaining their dietary health. With the right diet and care, your dog can enjoy a long, happy, and healthy life.
FAQs:
Q: How often should I give my dog bully sticks? A: Bully sticks can be given a few times a week as a treat, but should not replace a balanced diet.
Q: Are bully sticks safe for puppies? A: Yes, but choose bully sticks appropriate for your puppy’s size and supervise them while chewing.
Q: Can bully sticks help with my dog’s dental health? A: Yes, chewing on bully sticks helps reduce plaque and tartar buildup, promoting better dental health.
For more detailed information and resources, you can visit AKC, ASPCA, and Dog Nutrition.